Abstract
Background:
Prophylactic treatment with factor products has demonstrated superior outcomes and care compared to on-demand treatment in hemophilia patients, including patients with pre-existing joint diseases. However, 40% to 50% of severe or moderate hemophilia A and B patients are still treated on-demand in the US. Recombinant factor VIII and IX Fc fusion proteins (rFVIIIFc and rFIXFc) were the first extended half-life (EHL) products approved in the US (in 2014) with the promise of optimizing prophylactic regimens by achieving low bleeding rates and improving joint health with fewer injections overall.
Objective:
This is the first real-world study to assess the impact of EHL rFVIIIFc and rFIXFc on overall prophylaxis rates, particularly to understand how patients have transitioned from on-demand treatment.
Methods:
A retrospective analysis was conducted on aggregate, de-identified United States Specialty Pharmacy Provider (SPP) records from Jan 2014 to June 2018 (data pull on June 14th, 2018). Adult hemophilia patients (age 18 and above) were included for an analysis of treatment regimens prior to and after switching to EHL rFVIIIFc and rFIXFc (on-demand or prophylaxis). The results were descriptively compared to those who switch to the other EHL PEGylated rFVIII and rFIX albumin Fusion Protein (rFIX-FP) and conventional factors.
Results:
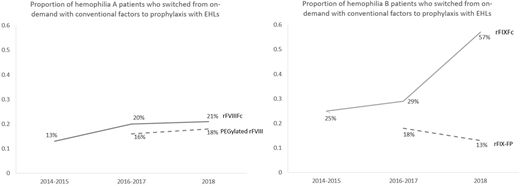
A total of 304 hemophilia A patients who switched to rFVIIIFc and 133 hemophilia B patients who switched to rFIXFc were included in this study. For the hemophilia A and B patients, the median age was 31 and 32 years and median weight was 82 and 79 kg. The proportion of patients who switched from on-demand treatment with conventional factors to prophylaxis treatment with EHL rFVIIIFc and rFIXFc among all patients who switched to these products increased over time since the FDA approval (3 time points: 2014-2015, 2016-2017, and 2018: rFVIIIFc: 13%, 20%, and 21%; rFIXFc: 25%, 29%, and 57%). Such proportions were higher compared to those who switched from on-demand with conventional factors to prophylaxis with the other EHLs (2016-2017, 2018: PEGylated rFVIII: 16%, 18%; rFIX-FP: 18%, 13%, see comparison in the Figure) and with conventional factors (2014-2015, 2016-2017, and 2018: conventional rFVIII: 10%, 7%, and 9%; conventional rFIX: sample size was too small and not suitable for analysis).
Discussion:
rFVIIIFc and rFIXFc have transformed the paradigm of hemophilia care by shifting on demand patients to prophylaxis significantly faster than conventional factors and any other EHLs to date. This shift is significant as it is helping more hemophilia patients achieve optimal protection through low bleeding rates and improved joint health over the long-term.
Jain:Bioverativ: Employment. Li:Bioverativ: Employment. Krishnan:Bioverativ: Employment. Hagberg:Bioverativ: Employment. Su:Bioverativ: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal